Introduction
Light intensity is a fundamental aspect of both natural and artificial environments. It influences human health, plant growth, workplace efficiency, and even technological innovations. Properly measuring light intensity ensures optimal lighting conditions in various fields, from interior design and industrial safety to medical applications and renewable energy solutions. Despite its significance, many people overlook the factors affecting light intensity and the best ways to measure it accurately.
In this guide, we will explore light intensity from a professional perspective, offering insights into key measurement techniques, the best instruments to use, and practical applications that impact everyday life. Whether you are a scientist, an engineer, a business owner, or just someone curious about how light affects your environment, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable knowledge.
Understanding Light Intensity
What is Light Intensity?
Light intensity, also referred to as illuminance, is the amount of light energy that falls on a surface per unit area. It is measured in lux (lx) or foot-candles (fc), with lux representing one lumen per square meter and foot-candle representing one lumen per square foot.
Beyond just measuring brightness, light intensity plays a crucial role in health, productivity, and sustainability. Poor lighting conditions can lead to eye strain, reduced work performance, and even psychological effects such as seasonal affective disorder (SAD). Understanding light intensity helps in optimizing environments for comfort and efficiency.
Factors Affecting Light Intensity
Several factors influence light intensity in different settings:
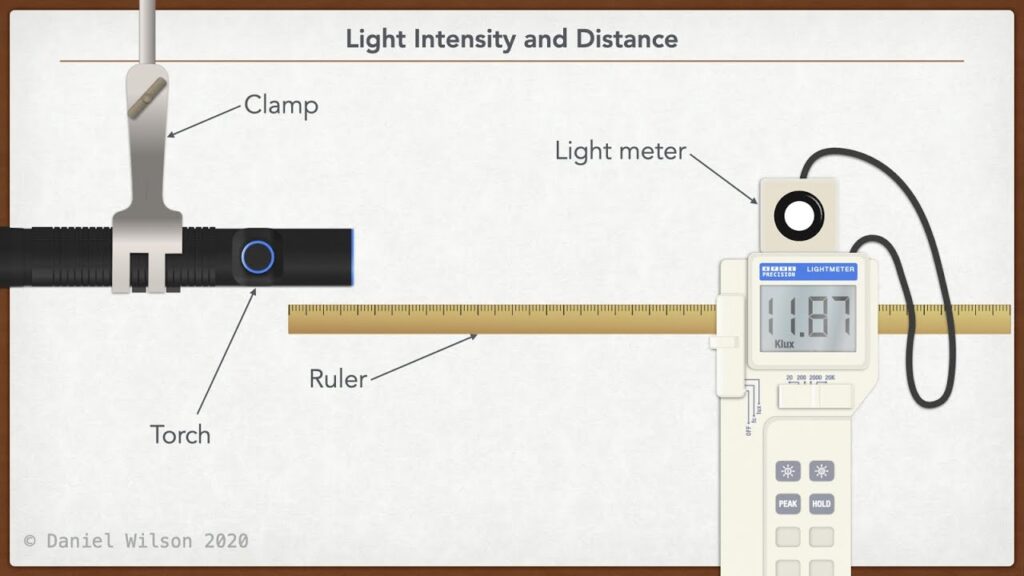
- Distance from the Light Source – Light intensity follows the inverse square law, meaning it decreases exponentially as the distance from the source increases.
- Type of Light Source – Natural sunlight, LED lights, fluorescent bulbs, and incandescent bulbs all emit different intensities and spectral distributions.
- Reflection and Absorption – Surfaces with high reflectivity, such as white walls, can increase intense pulsed light, while darker surfaces absorb more light, reducing overall illumination.
- Environmental Conditions – Weather, pollution, and atmospheric conditions, such as fog and dust, can affect the intensity and quality of light.
- Time of Day and Geographic Location – Natural intense pulsed light changes throughout the day and varies based on latitude and seasonal changes.
Techniques for Measuring Light Intensity
Lux Meters
Lux meters, or light meters, are the most common tools for measuring illuminance. They are widely used in workplaces, photography studios, and interior lighting design to ensure that lighting levels meet safety and efficiency standards.
Photodiodes
Photodiodes are semiconductor devices that convert light into an electrical current. These are commonly used in automation, scientific research, and industrial applications where precise and responsive light intensity measurements are necessary.
Pyranometers
Pyranometers are designed to measure solar radiation, making them essential tools in meteorology and solar energy applications. They help determine the effectiveness of solar panels and assess the impact of sunlight on environmental conditions.
Spectrophotometers
Spectrophotometers go beyond measuring just intensity; they analyze the full spectrum of light. These instruments are commonly used in laboratories for quality control, material testing, and medical diagnostics.
Instruments for Measuring Light Intensity
Digital Light Meters
Digital light meters provide instant readings of light intensity and often include additional features such as data logging, wireless connectivity, and adjustable settings for different environments.
Solarimeters
Solarimeters measure the total energy from sunlight, playing a crucial role in optimizing solar power systems and environmental monitoring.
Light Probes
Light probes are used in specialized applications, such as LED manufacturing and scientific experiments, where localized light intensity measurements are needed.
Factors to Consider When Measuring Light Intensity
Proper Positioning of the Measurement Device
To obtain accurate readings, the measuring instrument should be positioned correctly relative to the light source and target area. The angle and height of placement can significantly impact the results.
Calibration of the Instrument
Regular calibration ensures that measurement devices provide accurate and reliable data. Using a reference light source during calibration helps maintain consistency in readings.
Environmental Variables
Environmental factors such as humidity, temperature, and reflections can distort light measurements. Conducting measurements in controlled conditions minimizes errors.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Inaccurate Readings
Inaccurate measurements can be caused by device misalignment, improper calibration, or interference from external light sources. Double-checking setup conditions and recalibrating the device can resolve most issues.
Interference from Other Light Sources
Artificial lighting or reflections from nearby objects can skew measurements. Using shielding techniques or conducting tests in controlled lighting conditions helps mitigate interference.
Maintenance and Calibration
Regular maintenance, including cleaning sensors and updating calibration settings, ensures the long-term accuracy and reliability of intense pulsed light measurement instruments.
Real-World Applications of Light Intensity Measurement
Workplace and Occupational Safety
Regulations in industries such as manufacturing and healthcare mandate proper lighting levels to reduce eye strain and workplace accidents. Intense pulsed light measurement ensures compliance with safety standards.
Agriculture and Horticulture
Light intensity affects plant growth, photosynthesis rates, and crop yields. Farmers and horticulturists use light meters to optimize greenhouse conditions and improve agricultural productivity.
Photography and Film Production
In photography and videography, light intensity determines exposure settings, contrast, and overall image quality. Professional photographers use lux meters to perfect lighting conditions.
Medical and Scientific Research
From medical imaging to laboratory experiments, precise light measurements are critical in ensuring accurate results and advancing research in various scientific fields.
Smart Lighting and IoT Applications
With the rise of smart homes and IoT-enabled lighting systems, measuring light intensity helps automate brightness adjustments and enhance energy efficiency in residential and commercial spaces.
Conclusion
Accurately measuring light intensity is essential for optimizing various environments, from workplaces and homes to industrial and scientific settings. Using advanced instruments such as lux meters, photodiodes, pyranometers, and spectrophotometers, professionals can ensure appropriate lighting conditions for safety, efficiency, and productivity.
By understanding the factors affecting intense pulsed light and employing proper measurement techniques, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions that enhance well-being and energy efficiency. Whether you are an engineer, a photographer, a farmer, or an environmentalist, mastering light intensity measurement opens the door to a brighter and more sustainable future. Contact Rayera for more professional information.
Common Questions
1. Why is it important to measure light intensity?
Measuring light-intensity ensures optimal lighting conditions, enhances productivity, and promotes safety in various environments.
2. What are the different units used to measure light intensity?
The most common units are lux (lx) and foot-candles (fc), which represent lumens per square meter and lumens per square foot, respectively.
3. How can I calibrate a light measuring device?
Calibration involves using a reference light source and adjusting the instrument to ensure accurate readings.
4. What are the applications of measuring light intensity?
Its measurements are used in agriculture, photography, workplace safety, smart lighting, and scientific research.
5. How does light intensity affect plant growth?
It influences photosynthesis and plant health. Proper lighting levels enhance growth, while insufficient or excessive light can lead to plant stress and reduced yields.
Understanding light intensity and how to measure it effectively is essential for both everyday applications and advanced scientific research. By leveraging the right tools and techniques, anyone can optimize lighting conditions to achieve the best possible outcomes.